Consumer's Equilibrium utility Analysis|Who is the consumer ?|What is meant by utility ?
Who is the consumer ?
Any person who buys and consumes goods and services for consumption. It is called consumer.
What is meant by utility ?
Utility refers to the satisfaction derived from the consumption of something.
How is utility measured ?
Utility is measured in two ways.
i) Quantitative measure of utility
ii) Ordinal measure of utility
Quantitative measure of utility
The countable measure of utility means the measure of utility in countable numbers or units; Like - can be measured in the form of 1,2,3.
Ordinal measure of utility
Ordinal measured means that utility can only be given as an order according to the level of satisfaction; it cannot be expressed in terms of units like 1,2,3.
How many types of utility are there ?
There are three types of utility.
i) Total utility
ii ) Marginal utility
iii) Average utility
Total utility
It is the sum total of the utility derived from consuming all the units of a commodity.
TU =∑MU
Marginal utility
The additional utility derived from consuming one more unit of a commodity.
MUnth =TUn-TUn-1
Average utility
The quotient obtained by dividing total utility by different units of a commodity is called average utility.
Table: Relationship between total utility and marginal utility
picture interpretation
i) Total Utility = Sum of Marginal Utility
ii) Total utility goes on increasing as long as marginal utility is positive.
iii) When marginal utility is zero, then total utility is maximum.
iv) When marginal utility is negative, then total utility phenomenon begins.
consumer equilibrium in a commodity situation
Example
So as we see here that MUx/MUm=Px is equal to the consumer is in equilibrium in case of a commodity.
If MUx/MUm≠Px is not equal to Px then the consumer is not in equilibrium in the case of a good. Due to which two situations arise.
Case I
This situation induces consumers to buy more and more units of good-X and according to the law of diminishing marginal utility, as they go on consuming more units of good-X until Mux/Mum = px.
Case II
This situation induces the consumer to buy less quantity of the good. According to the law of diminishing marginal utility, as the consumption of good X increases, the consumer consumes good-X until Mux/MUm.
consumer equilibrium in case of two goods
If there is no balance in the position of the two goods of the consumer, then due to which two situations arise.
Case I
In this situation the consumer will spend more on good X. As consumption of good X increases, MUx will fall. On the other hand, consumption of good y will fall.MUy will increase. This process will continue until Conditions are not met.
Case II
In this situation the consumer will spend more on good Y. As consumption of good y increases, MUy will fall. On the other hand, consumption of good X will fall and MUx will increase. This process will continue until the conditions are met.


.png)

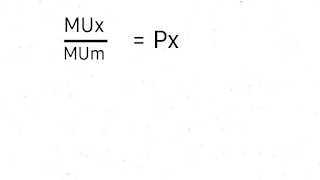
.png)


